Systemic lupus erythematosus, referred to as SLE or lupus, is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation, pain and swelling in various parts of the body and can damage many organs of the body.
In addition to affecting the skin and joints, it can affect other organs such as the kidneys, the tissue lining the lungs (pleura), the pericardium around the heart and the brain and often leads to inflammation of the blood vessels (vasculitis). Most patients feel fatigue and have rashes, arthritis (painful and swollen joints) and low-grade fever.
SLE is caused by antibodies produced in response to self-tissue which end up in cells in organs, where they damage those tissues. The cause of lupus is unknown but like other autoimmune diseases, most likely results from a combination of genetics and environmental factors, including chronic viral infections, toxic exposures and certain medications. Lupus usually starts in people in their 20s and 30s, affects women more than men and is more common in some ethnic groups.
Lupus flare-ups vary from mild to severe. Most patients have times when the disease is active, followed by times when the disease is inactive (remission).
A comprehensive approach to the management of complex conditions such as autoimmune disease must take into consideration many aspects of health, including gut barrier integrity and imbalances of gut flora, liver detoxification capacity and toxic burden, hormone imbalances, energy production capacity, nutrient status and most importantly, immune imbalances which promote autoimmune states. More specifically, Functional Medicine approaches autoimmune disease by identifying the triggers and mediators of the autoimmune attacks, minimizing the self-destructive immune responses and enhancing the body’s ability to recover from flare-ups.
There are 4 areas of management of autoimmune conditions in the Functional Medicine approach:
Lab testing is a critical first step in identifying the extent of systemic inflammation and ruling out many environmental insults which act as triggers and mediators of autoimmunity, such as chronic infection, heavy metal toxicity and decreased capacity to perform liver detoxification. Food sensitivities can also promote inflammation and potentially drive autoimmune responses. Identifying and addressing these issues is critical in autoimmune patients to minimize damage and promote restorative function.
Functional Medicine addresses diet and lifestyle issues as well as using anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating herbs and nutritional compounds to decrease immune responses to self-tissue. Identifying the triggers of autoimmunity and modulating the immune response can have powerful long-term positive effects on slowing or stopping tissue destruction and improving quality of life.
There are a number of natural compounds that help support a faster recovery by breaking down offending triggers, increasing blood flow to target tissue, and dampening the immune response.
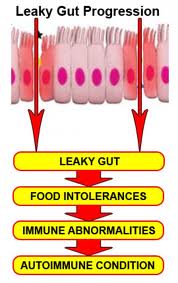 Addressing Associated Conditions and Promote Autoimmune Responses
Addressing Associated Conditions and Promote Autoimmune ResponsesThere is growing evidence that increased intestinal permeability plays a pathogenic role in various autoimmune diseases. Increased intestinal permeability and compromised gut integrity appears to precede AI disease and predisposes to immune activation and chronic inflammation. Assessment and proper restoration of the integrity of the intestinal barrier is crucial in managing autoimmune conditions. Read More on Leaky Gut
There is growing evidence that increased intestinal permeability plays a pathogenic role in various autoimmune diseases. Identifying the existence of intestinal permeability and addressing this condition, leads to a more comprehensive and satisfactory outcome in the autoimmune patient.
Milpitas: 408-262-6606
1649 S. Main Street, Ste. 102
Milpitas, CA 95035
Oakland: 510-350-8082
6232 La Salle Ave
Oakland, CA 94611